

- ARPSPOOF ALL CLIENTS HOW TO
- ARPSPOOF ALL CLIENTS SOFTWARE
- ARPSPOOF ALL CLIENTS CODE
Ether extracted from open source projects.
 Espionage is a network packet sniffer that intercepts large amounts of data being passed through an interface.
Espionage is a network packet sniffer that intercepts large amounts of data being passed through an interface. ARPSPOOF ALL CLIENTS HOW TO
In this text I will show you how to use it for network communication in 802.
ARPSPOOF ALL CLIENTS CODE
send (packet, verbose=False) After performing all the above steps, our code will look something like.
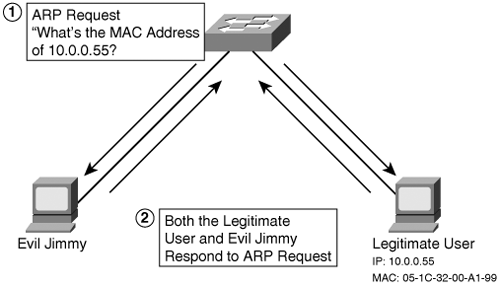
Use cryptographic network protocols: Transport Layer Security (TLS), Secure Shell (SSH), HTTP Secure (HTTPS) and other secure communications protocols bolster ARP spoofing attack prevention by encrypting data prior to transmission and authenticating data when it is received.Ĭlick here to learn how we can help strengthen web application security and protect applications from attack.Arp spoofing python scapy (“IP forwarding” is a synonym for “routing. These programs work by inspecting and certifying data before it is transmitted and blocking data that appears to be spoofed. Use ARP spoofing detection software: There are many programs available that help organizations detect ARP spoofing attacks. Trust relationships rely only on IP addresses for authentication, making it significantly easier for attackers to run ARP spoofing attacks when they are in place. Avoid trust relationships: Organizations should develop protocols that rely on trust relationships as little as possible. Packet filters are useful in ARP spoofing prevention because they are capable of filtering out and blocking packets with conflicting source address information (packets from outside the network that show source addresses from inside the network and vice-versa). Packet filtering: Packet filters inspect packets as they are transmitted across a network. The following methods are recommended measures for detecting, preventing and protecting against ARP spoofing attacks: From here, the attacker can steal data or launch a more sophisticated follow-up attack.ĪRP Spoofing Detection, Prevention and Protection  As other hosts on the LAN cache the spoofed ARP packets, data that those hosts send to the victim will go to the attacker instead. The attacker chooses its target and begins sending ARP packets across the LAN that contain the attacker’s MAC address and the target’s IP address. The attacker uses the ARP spoofing tool to scan for the IP and MAC addresses of hosts in the target’s subnet.
As other hosts on the LAN cache the spoofed ARP packets, data that those hosts send to the victim will go to the attacker instead. The attacker chooses its target and begins sending ARP packets across the LAN that contain the attacker’s MAC address and the target’s IP address. The attacker uses the ARP spoofing tool to scan for the IP and MAC addresses of hosts in the target’s subnet. ARPSPOOF ALL CLIENTS SOFTWARE
Examples of popular ARP spoofing software include Arpspoof, Cain & Abel, Arpoison and Ettercap.
The attacker opens an ARP spoofing tool and sets the tool’s IP address to match the IP subnet of a target. The steps to an ARP spoofing attack usually include: Man-in-the-middle attacks: MITM attacks can rely on ARP spoofing to intercept and modify traffic between victims.ĪRP spoofing attacks typically follow a similar progression. Session hijacking: Session hijacking attacks can use ARP spoofing to steal session IDs, granting attackers access to private systems and data. As a result, traffic that is intended for many different IP addresses will be redirected to the target’s MAC address, overloading the target with traffic. 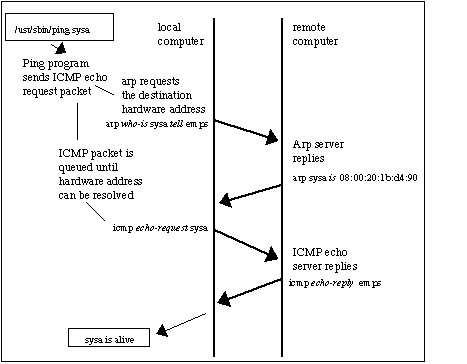 Denial-of-service attacks: DoS attacks often leverage ARP spoofing to link multiple IP addresses with a single target’s MAC address. Beyond this, ARP spoofing attacks are often used to facilitate other attacks such as: In their most basic application, ARP spoofing attacks are used to steal sensitive information. The effects of ARP spoofing attacks can have serious implications for enterprises.
Denial-of-service attacks: DoS attacks often leverage ARP spoofing to link multiple IP addresses with a single target’s MAC address. Beyond this, ARP spoofing attacks are often used to facilitate other attacks such as: In their most basic application, ARP spoofing attacks are used to steal sensitive information. The effects of ARP spoofing attacks can have serious implications for enterprises.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
